A patented technology, a unique know-how
The microorganism detection system developed by Microbia Environnement is based on genetic barcodes readable using colometric tests.

A genetic barcode is a very specific sequence, a “signature”, in the genetic materials of a determined microorganism. Our technology enables a highly-sensitive recognition of this marker thanks to a molecular tool named biosensor.
The performance of the biosensors we design relies on precise targeting and quantification of microbial ribosomal RNA (rRNA), a constitutive molecule of the ribosomes, that are the cell “factories” catalysing the protein production, then representative of the cellular activity.
An increase of the activity signing most of the time an exponential population growth and/or a higher biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, its detection permits to anticipate the occurence of a proliferation phenomenon and to prevent the risk associated with toxic compounds release.
Inspired by state-of-the-art methods used in biomedical research, our approach provides not only a basic analysis of microbial contamination in water but a powerful diagnosis and forecasting tool of the water quality in a context of environmental risk assessment.
How it works…
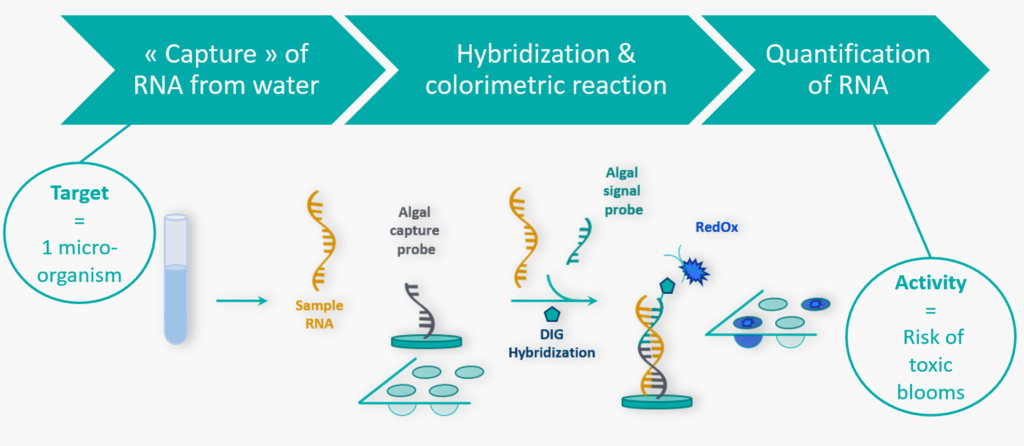
A so-called biosensor consists of genetic materials fixed on a solid substrate that bind specifically free genetic elements extracted from the water sample.
Our biosensors are designed to “capture” ribosomal RNA (rRNA) of pre-defined microalgae or cyanobacteria species known to produce toxins.
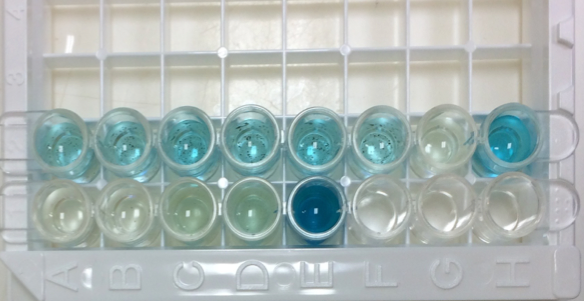
Following an ELISA* sandwich hybridization assay (SHA), a second genetic probe, free and coupled with an enzymatic activity recognizes and binds as well to the sampled rRNA previously captured, forming a triplet (see Figure).
By adding substrate, we detect the desired enzymatic reaction that induces a colorimetric signal proportional to the quantity of sampled rRNA. Interpolation of data using a calibration step is used to finally estimate the activity of the considered micro-organism(s).
*enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
And, it’s fast!
The estimation of cellular activity is achieved in less than 2 hours after RNA extraction from water samples.

